Why is a Reliable Payment Gateway Key to E-Commerce Success?

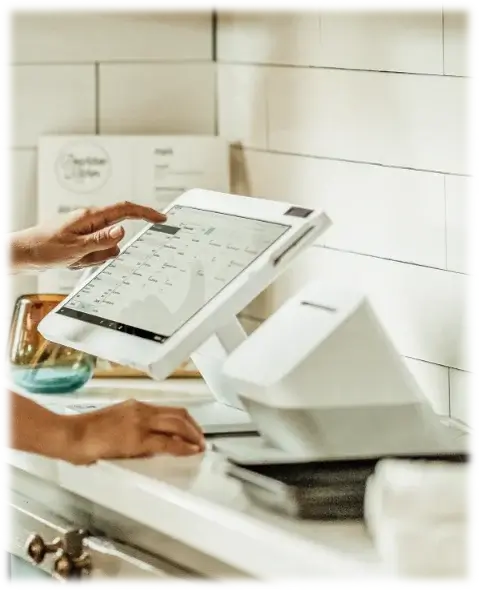
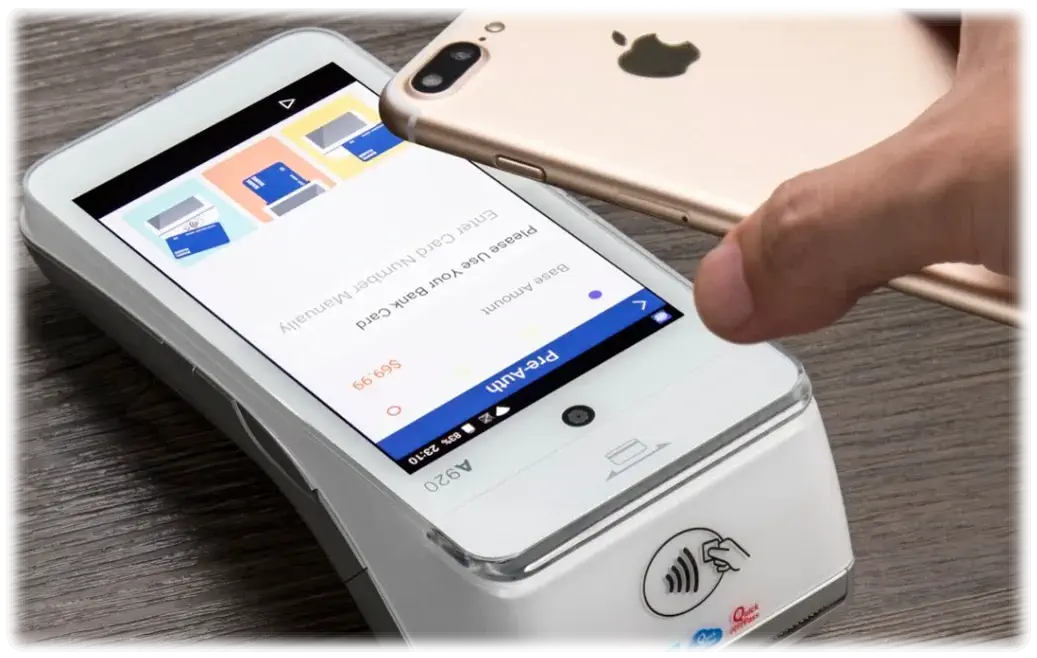
Digital payments have become a new normal in the modern economy, and payment gateways serve as a cornerstone of this system. Whether you run an online business or have a brick-and-mortar store, payment gateways are essential to facilitate smooth cashless transactions. They function as a digital bridge that authorizes and processes payments securely and quickly.
If you're considering adopting an online payment system for your business, this guide will explain everything you need to know in simple terms—no tech jargon or prior subject knowledge required. Understanding payment gateways better will empower you to make smarter business decisions! So, let’s dive into how payment gateways work, their types, benefits, limitations, and tips for choosing the best one for your business.
What is a Payment Gateway?
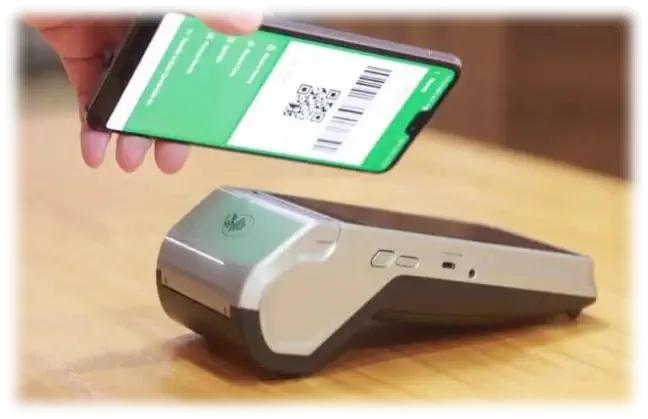
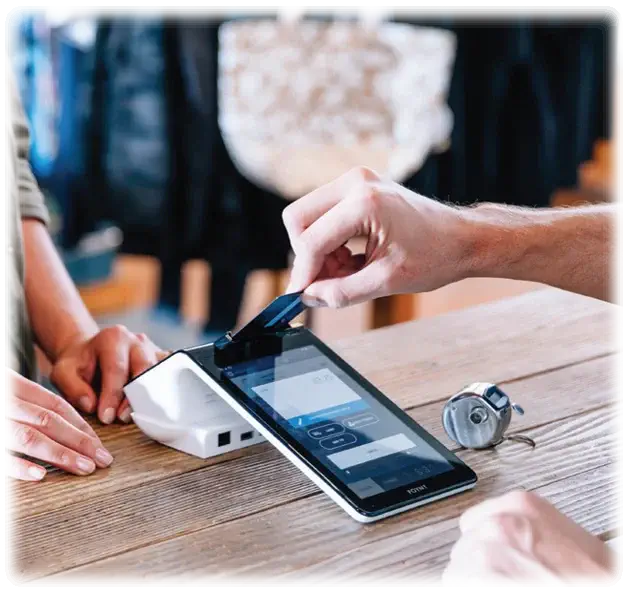
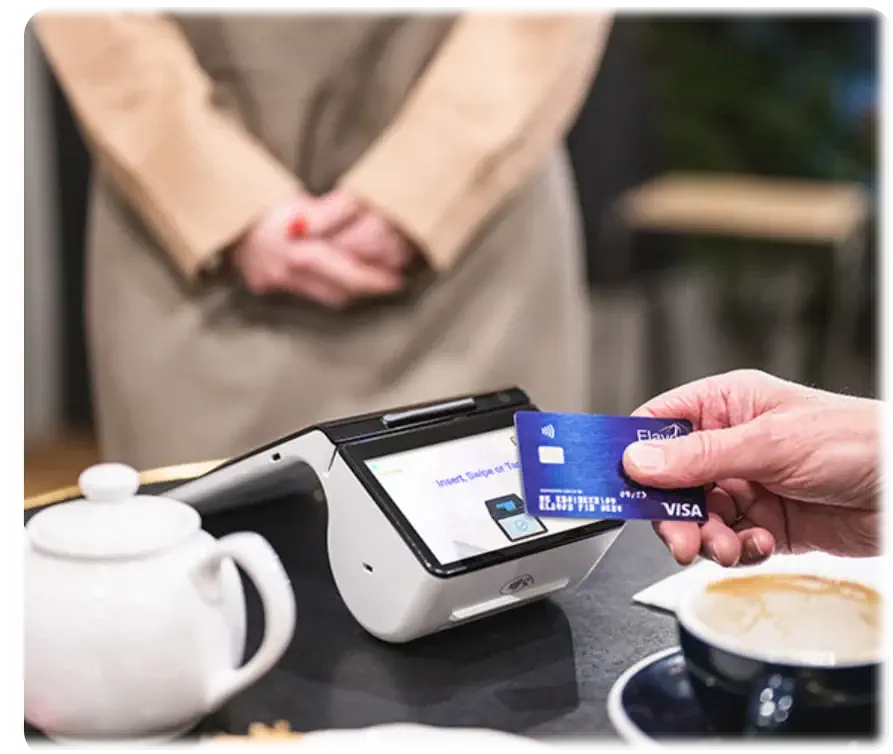
Let’s begin with breaking down the basic concept of payment gateways. A payment gateway is a merchant service that enables electronic payments, including credit and debit card payments, digital wallets, e-checks, Gift card payments, and in-person payments.
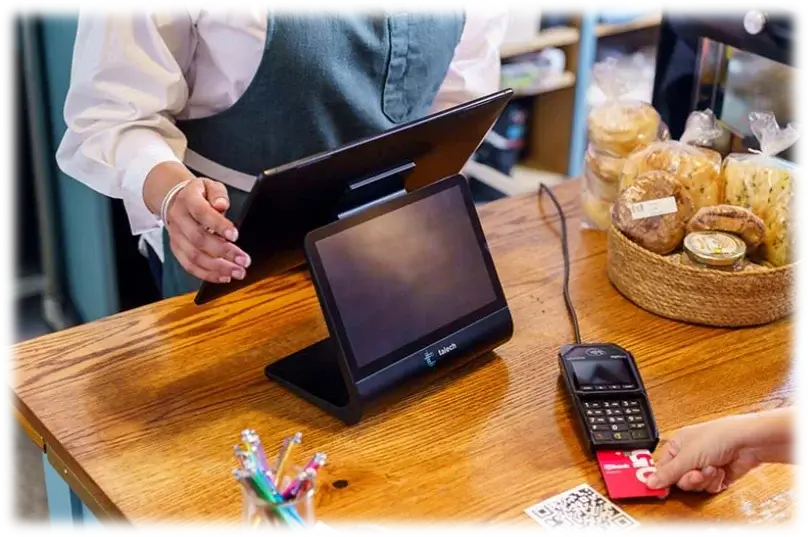
Think of it as the cash register of the digital world, a front-end mechanism for collecting, transferring, and authorizing payment data. It communicates between the customers’ banks, the business’s bank, and the payment processor. Whether it’s an e-commerce site, a mobile application, or an in-store transaction, a payment gateway ensures that payments are processed quickly and securely.
How Payment Gateways Work: The Typical Transaction Process
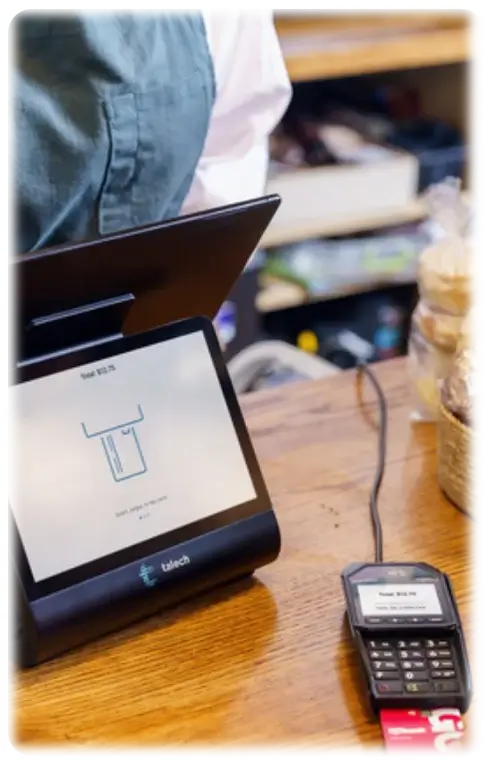
When a customer places an order, a payment gateway initiates a series of steps to process the transaction. Here is a process overview to help you understand how exactly things work with a payment gateway.
1. Order Placement: A customer places an order and proceeds to payment.
2. Data Transmission: The gateway securely collects transaction details, sometimes bypassing the merchant’s server for added security.
3. Format Conversion: Next, the payment gateway reformats the payment data into a language the bank understands.
4. Bank Communication: The payment information is then sent to the bank that works with your credit card (like Visa or Mastercard) to check if your bank can allow the payment.
5. Authorization Response: Your bank checks if you have enough money or credit and then tells the payment system whether to proceed or if the payment should be stopped.
6. Order Fulfillment: Approved transactions are finalized, and funds are eventually settled into the merchant’s account.
The entire process is typically completed within seconds, ensuring a swift checkout experience for customers.
Types of Payment Gateways
Payment gateways can be broadly categorized into three types based on where the transaction data is processed. Let’s go through these:
On-Site Payments
Large businesses often opt for on-site payment gateways, where payment data is processed directly on their servers. This option offers full control over the payment experience but comes with higher responsibility for security and compliance.
On-Site Checkout, Off-Site Payments
This hybrid approach allows customers to complete checkout on the merchant’s site, but payment processing happens off-site. It simplifies security management for the merchant but limits control over the end-to-end user experience.
Redirect Gateways
Redirects transfer customers to a third-party platform (e.g., PayPal) to complete the transaction. These gateways are simple and secure, ideal for small businesses, but may introduce additional steps for customers.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway is critical to ensuring a smooth and secure customer experience. Consider these factors:
Customer Payment Preferences
Understand your customers' preferred payment methods—credit cards, digital wallets, or alternative payment systems—and ensure your gateway supports them.
Integration with Existing Systems
Ensure the gateway integrates seamlessly with your platform, whether it’s an e-commerce website, mobile app, or point-of-sale (POS) system. Look for customizable solutions to streamline operations.
Security Measures
To protect sensitive data, opt for PCI DSS-compliant gateways with advanced encryption standards. Also, evaluate the gateway’s track record for security breaches.
Global Compatibility
For businesses with international customers, select gateways supporting multi-currency transactions and region-specific payment options like Alipay or Klarna.
Fees and Costs
Balance transaction fees with the security and features offered. For example, a lower fee gateway might increase costs if you need additional fraud prevention tools.
Reputation and Customer Trust
Choose well-known gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Authorize.net to reassure customers of the safety of their data.
Overcoming Payment Gateway Limitations
While payment gateways simplify transactions, they come with some limitations:
- Incomplete Card Coverage: Many gateways don’t support all card types or payment methods.
- Cross-Border Challenges: International payments can incur higher fees and compatibility issues.
- Security Risks: Despite encryption, gateways remain susceptible to breaches and malware.
A strategy to mitigate these issues is to stack multiple payment gateways or choose one that offers a well-rounded payment solution. By choosing the right payment solution provider, businesses can offer diverse payment options, improve user experience, and reduce the risk of disruptions.
Final Thoughts
In the digital era, the right payment gateway is more than a tool—it’s a strategic asset for your business. It simplifies transactions, boosts customer trust, and enhances security. With platforms like Thrifty Payments offering convenient payment solutions for different types of businesses, you can cater to global audiences and streamline your payment processes with ease.
FAQs About Payment Gateways
What is the best payment gateway?
The best gateway depends on your business needs. You should analyze your payment preference and employ a trusted gateway to cater to it.
Can payment gateways handle international payments?
Yes, many gateways support multi-currency transactions and region-specific options.
How do payment gateways impact transaction fees?
Gateways may charge flat or percentage-based fees, with additional costs for cross-border transactions or currency conversion.
By carefully evaluating your options, you can find a payment gateway that meets your business’s unique requirements while keeping your customers happy and secure. Digital payments have become a new normal in the modern economy, and payment gateways serve as a cornerstone of this system. Whether you run an online business or have a brick-and-mortar store, payment gateways are essential to facilitate smooth cashless transactions. They function as a digital bridge that authorizes and processes payments securely and quickly.
If you're considering adopting an online payment system for your business, this guide will explain everything you need to know in simple terms—no tech jargon or prior subject knowledge required. Understanding payment gateways better will empower you to make smarter business decisions! So, let’s dive into how payment gateways work, their types, benefits, limitations, and tips for choosing the best one for your business.
What is a Payment Gateway?
Let’s begin with breaking down the basic concept of payment gateways. A payment gateway is a merchant service that enables electronic payments, including credit and debit card payments, digital wallets, e-checks, Gift card payments, and in-person payments.
Think of it as the cash register of the digital world, a front-end mechanism for collecting, transferring, and authorizing payment data. It communicates between the customers’ banks, the business’s bank, and the payment processor. Whether it’s an e-commerce site, a mobile application, or an in-store transaction, a payment gateway ensures that payments are processed quickly and securely.
How Payment Gateways Work: The Typical Transaction Process
When a customer places an order, a payment gateway initiates a series of steps to process the transaction. Here is a process overview to help you understand how exactly things work with a payment gateway.
1. Order Placement: A customer places an order and proceeds to payment.
2. Data Transmission: The gateway securely collects transaction details, sometimes bypassing the merchant’s server for added security.
3. Format Conversion: Next, the payment gateway reformats the payment data into a language the bank understands.
4. Bank Communication: The payment information is then sent to the bank that works with your credit card (like Visa or Mastercard) to check if your bank can allow the payment.
5. Authorization Response: Your bank checks if you have enough money or credit and then tells the payment system whether to proceed or if the payment should be stopped.
6. Order Fulfillment: Approved transactions are finalized, and funds are eventually settled into the merchant’s account.
The entire process is typically completed within seconds, ensuring a swift checkout experience for customers.
Types of Payment Gateways
Payment gateways can be broadly categorized into three types based on where the transaction data is processed. Let’s go through these:
On-Site Payments
Large businesses often opt for on-site payment gateways, where payment data is processed directly on their servers. This option offers full control over the payment experience but comes with higher responsibility for security and compliance.
On-Site Checkout, Off-Site Payments
This hybrid approach allows customers to complete checkout on the merchant’s site, but payment processing happens off-site. It simplifies security management for the merchant but limits control over the end-to-end user experience.
Redirect Gateways
Redirects transfer customers to a third-party platform (e.g., PayPal) to complete the transaction. These gateways are simple and secure, ideal for small businesses, but may introduce additional steps for customers.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway is critical to ensuring a smooth and secure customer experience. Consider these factors:
Customer Payment Preferences
Understand your customers' preferred payment methods—credit cards, digital wallets, or alternative payment systems—and ensure your gateway supports them.
Integration with Existing Systems
Ensure the gateway integrates seamlessly with your platform, whether it’s an e-commerce website, mobile app, or point-of-sale (POS) system. Look for customizable solutions to streamline operations.
Security Measures
To protect sensitive data, opt for PCI DSS-compliant gateways with advanced encryption standards. Also, evaluate the gateway’s track record for security breaches.
Global Compatibility
For businesses with international customers, select gateways supporting multi-currency transactions and region-specific payment options like Alipay or Klarna.
Fees and Costs
Balance transaction fees with the security and features offered. For example, a lower fee gateway might increase costs if you need additional fraud prevention tools.
Reputation and Customer Trust
Choose well-known gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Authorize.net to reassure customers of the safety of their data.
Overcoming Payment Gateway Limitations
While payment gateways simplify transactions, they come with some limitations:
- Incomplete Card Coverage: Many gateways don’t support all card types or payment methods.
- Cross-Border Challenges: International payments can incur higher fees and compatibility issues.
- Security Risks: Despite encryption, gateways remain susceptible to breaches and malware.
A strategy to mitigate these issues is to stack multiple payment gateways or choose one that offers a well-rounded payment solution. By choosing the right payment solution provider, businesses can offer diverse payment options, improve user experience, and reduce the risk of disruptions.
Final Thoughts
In the digital era, the right payment gateway is more than a tool—it’s a strategic asset for your business. It simplifies transactions, boosts customer trust, and enhances security. With platforms like Thrifty Payments offering convenient payment solutions for different types of businesses, you can cater to global audiences and streamline your payment processes with ease.
FAQs About Payment Gateways
What is the best payment gateway?
The best gateway depends on your business needs. You should analyze your payment preference and employ a trusted gateway to cater to it.
Can payment gateways handle international payments?
Yes, many gateways support multi-currency transactions and region-specific options.
How do payment gateways impact transaction fees?
Gateways may charge flat or percentage-based fees, with additional costs for cross-border transactions or currency conversion.
By carefully evaluating your options, you can find a payment gateway that meets your business’s unique requirements while keeping your customers happy and secure.