An informative guide for payment gateway providers

As the Internet grew and online shopping became more common, businesses needed a secure method to accept online payments. CyberCash was a trailblazer in addressing these problems. It created the foundation for modern payment gateway providers with robust and safe functionality.
Online companies can now integrate a variety of payment gateways into their websites to accept payments. This blog provides a thorough tutorial on integrating payments into your website and best practices for safely collecting them.
While considering payment-processing options, you may have heard of a payment gateway. However, what is it, and why is it crucial for your company? The best payment processor for small businesses is the secret to giving clients a quick, secure, and dependable way to complete transactions. There has never been a greater need for safe and effective payment gateways, as there are predicted to be 555 million payment terminals globally by 2026.
This guide will explain the importance of payment gateways for your company's operations, how they protect sensitive data, and how to choose the best suits your requirements.
What is a gateway for payments?
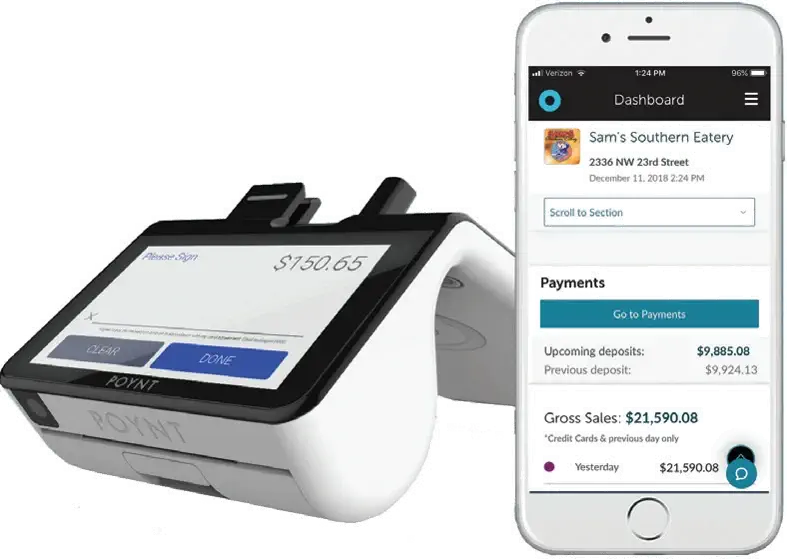
In a few words, a payment gateway acts as a safe intermediary that sends your customers' payment details to the bank for processing. Whether your client uses a credit card, debit card, or mobile device, the payment gateway guarantees a safe and easy transaction.
Alongside the growth of Internet commerce in the mid-1990s, payment gateways initially appeared. As early e-commerce sites like Amazon began to expand gradually, safe payment processing solutions were necessary. Thanks to early payment gateways, companies could, for the first time, handle credit card payments online.
These systems have changed, including quicker processing speeds, fraud detection technologies, and tighter encryption. They manage billions of transactions worldwide and accept various payment options, including mobile payments, digital wallets, and credit cards.
Examples of Payment Gateways: Typical Business Situations
Payment gateways are valuable tools for facilitating safe and efficient transactions in various sectors. Payment gateways guarantee that consumers can swiftly and securely make payments using any method, whether through mobile enterprises or online retailers. The following are some instances of various business settings where payment gateways are utilized:
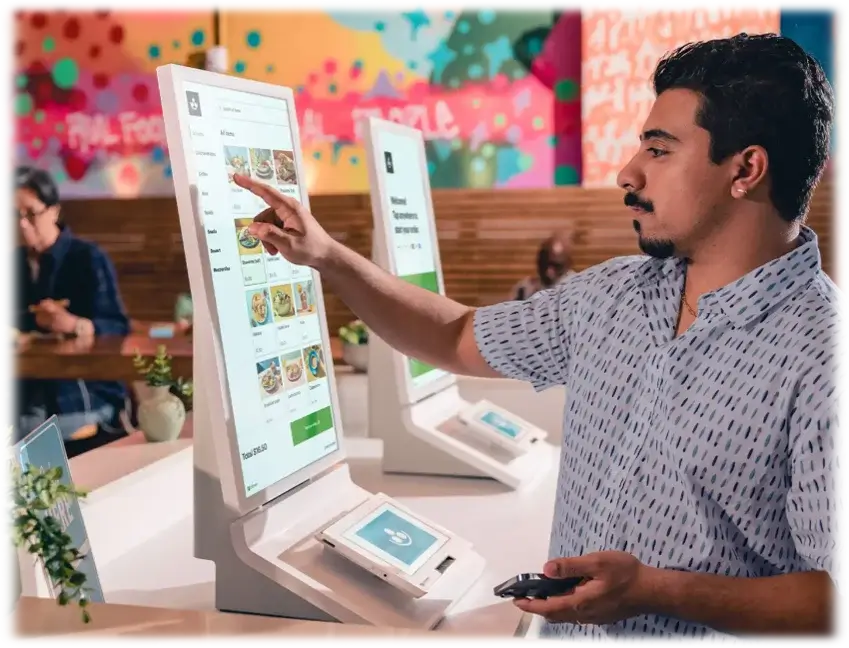
1. Internet-Based Shop
If you own an online apparel store, payment gateway providers let your clients enter their payment information at the point of sale. It makes purchasing simple and safe by swiftly processing the payment and validating their details.
2. Mobile Enterprise
Mobile payment gateways enable you to take payments anywhere using your phone or tablet, whether you operate a service-based business or have a food truck. These gateways allow speedy and flexible transactions, enabling you to serve clients constantly.
3. Services via Subscription
Payment gateways manage recurring payments automatically for companies that provide subscription services, such as monthly product boxes or streaming platforms. It guarantees that your clients receive monthly bills without updating their data, which is convenient for both of you.
4. Electronic Products and Services
If your company sells digital products such as software, music, or online courses, a payment gateway enables immediate access to these items following payment confirmation. Consumers can immediately receive their digital purchases, streamlining the procedure.
5. Platforms for Marketplaces
A payment gateway is essential for online marketplaces that link buyers and sellers (like eBay or Etsy) to manage numerous transactions between various parties safely. It guarantees that every transaction is handled independently and that the money is sent to the right sellers.
6. Foreign Exchange
If your company caters to clients worldwide, a payment gateway with multi-currency compatibility facilitates seamless international transactions. It instantly converts payments into the appropriate currency, providing a hassle-free experience for you and your clients.
How Do Gateways for Payments Operate?
A Payment gateway securely shares Sensitive payment information between your company and the bank. This is a more thorough explanation of how it operates:
1. The client places an order
Whether the platform is an online store, app, or in-store system, the user starts a transaction by inputting their payment information (credit card, debit card, or another payment method).
2. Payment Gateway for Platform Contacts
The platform (e-commerce website, mobile application, or point-of-sale system) transmits the payment information to the payment gateway after completing the transaction. The gateway protects the customer's data during transactions by securely encrypting it.
3. Payment Gateway Issuing Bank Contacts
The payment gateway sends the transaction request to the issuing bank (the customer's bank). The issuing bank checks for fraud and confirms that the consumer has enough money or credit.
4. Payment Confirmed by the Bank
If the transaction is accepted, the issuing bank returns a confirmation message to the payment gateway. The bank may reject the transaction if fraud or insufficient money is discovered.
5. Response from Payment Gateway
Following the bank's confirmation receipt, the payment gateway notifies the platform whether the payment was accepted or denied.
6. Payment to the Merchant
If the payment is accepted, the money is sent to the merchant's account from the issuing bank. The merchant can now validate the order and start the fulfillment process.